EMT trauma scenarios simulate real-life emergencies, preparing responders for high-pressure situations; These exercises focus on patient assessment, injury management, and decision-making under stress. Realistic simulations enhance critical thinking and practical skills, ensuring effective trauma care delivery in emergency settings.
1.1. Overview of Trauma Scenarios in EMT Training
EMT trauma scenarios are simulated real-life emergencies designed to prepare responders for critical situations. These exercises often involve injuries from car accidents, falls, or assaults. Trainees practice patient assessment, stabilization, and transport techniques. Simulation-based learning allows EMTs to develop decision-making skills in high-pressure environments. Realistic scenarios, including multiple casualties, enhance their ability to prioritize care. These training modules emphasize hands-on experience, ensuring EMTs are equipped to handle diverse trauma cases effectively. The goal is to improve critical thinking and adaptability, crucial for saving lives in emergency settings.
1.2. Importance of Simulation-Based Learning in Trauma Care
Simulation-based learning is vital for EMT training, offering a controlled environment to practice high-stakes trauma care; Realistic scenarios expose trainees to diverse injuries, enhancing their ability to diagnose and treat effectively. Hands-on experience builds confidence and competence, reducing errors in real emergencies. Interactive simulations also foster teamwork and communication, essential for patient outcomes. By replicating real-life conditions, simulation training ensures EMTs are prepared to respond efficiently and accurately during critical incidents.
Common EMT Trauma Scenarios
Common EMT trauma scenarios include motor vehicle collisions, falls, and penetrating injuries. These situations require rapid assessment and intervention to stabilize patients effectively in emergency settings.
2.1. High-Fidelity Simulation of Traumatic Injuries
High-fidelity simulation in EMT training replicates traumatic injuries with lifelike detail, allowing responders to practice advanced care techniques. These simulations include realistic anatomical models and dynamic patient responses, enhancing learning outcomes. By immersing EMTs in scenarios like severe lacerations, fractures, or internal bleeding, they gain hands-on experience in stabilizing patients and managing complex trauma cases effectively. This approach bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, ensuring better preparedness for real-life emergencies. Realistic simulations also foster critical thinking and improve decision-making under pressure, which are essential for trauma care.
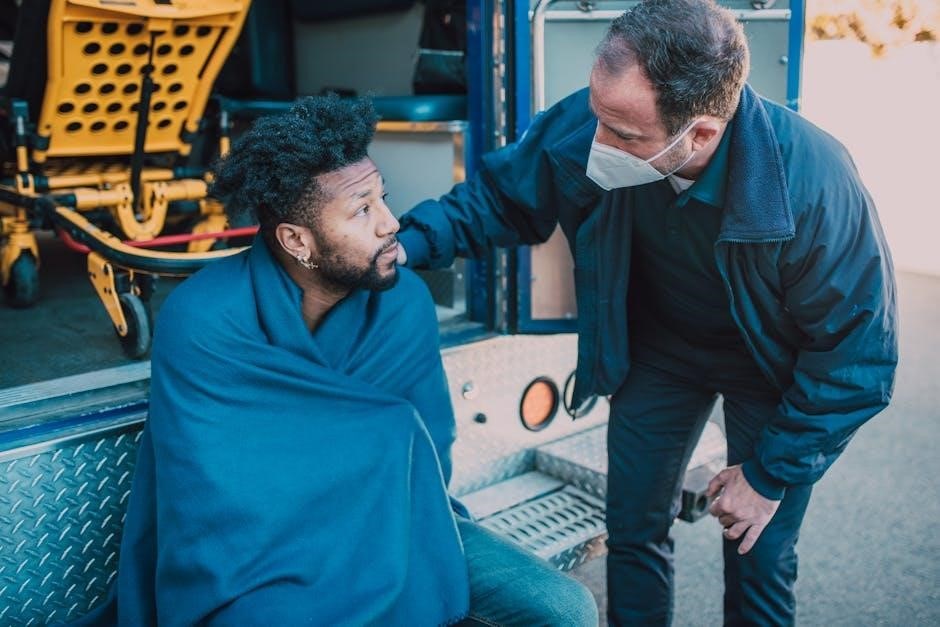

2.2. Real-Life Applications of Trauma Scenarios in EMT Training
Trauma scenarios in EMT training mirror real-life emergencies, equipping responders with practical skills. From patient assessment drills to high-pressure simulations, these exercises prepare EMTs for situations like severe injuries, cardiac arrests, and electric shock. Real-time medical emergencies, such as those experienced during training events like “Trauma Island,” allow EMTs to practice interventions in immersive environments. These applications ensure that responders are adept at handling diverse trauma cases, improving decision-making and care delivery in actual emergencies. Realistic training fosters confidence and competence, enabling EMTs to provide effective care in critical situations.
EMT Training Programs and Trauma Simulation
EMT training programs integrate trauma simulation to enhance preparedness for real-life emergencies. Structured modules and hands-on exercises ensure responders are skilled in assessing and managing traumatic injuries effectively.

3.1. Structured Training Modules for Trauma Response
Structured training modules for trauma response provide a standardized framework for EMTs to master essential skills. These modules often include simulation tools, hands-on practice, and scenario-based drills. By replicating real-life emergencies, trainees develop the ability to assess and manage traumatic injuries systematically. The curriculum is designed to ensure proficiency in prioritizing care, stabilizing patients, and making quick decisions. These modules also incorporate feedback mechanisms to refine techniques and improve performance. Regular assessments and practical exercises ensure EMTs are well-prepared to handle diverse trauma scenarios effectively in the field.

3.2. Hands-On Experience with Real-Time Medical Emergencies
Hands-on experience with real-time medical emergencies is crucial for EMT training. Simulation drills mimic high-stress scenarios, enabling trainees to practice trauma assessments, injury management, and life-saving interventions. Real-time feedback from instructors helps refine techniques and decision-making. Trainees engage with advanced tools like point-of-care ultrasonography and ALS equipment, enhancing their proficiency. These exercises foster adaptability and confidence, preparing EMTs to respond effectively in dynamic, unpredictable environments. Practical exposure ensures they can apply learned skills seamlessly during actual emergencies, improving patient outcomes and operational efficiency in the field.
Patient Assessment in Trauma Scenarios
Patient assessment in trauma scenarios involves dynamic techniques to identify injuries quickly. Tools like FAST enhance evaluation, ensuring timely and accurate interventions in critical situations.
4.1. Dynamic Patient Assessment Techniques
Dynamic patient assessment techniques are essential in trauma scenarios, emphasizing real-time evaluation of a patient’s condition. These methods combine visual, auditory, and tactile cues to quickly identify injuries. EMTs use these techniques to prioritize care, ensuring timely interventions. Hands-on experience and simulation training enhance proficiency in dynamic assessments. Such approaches improve patient outcomes by focusing on critical areas like breathing, circulation, and neurological status; Integrating these techniques into training prepares EMTs to handle unpredictable trauma scenarios effectively, ensuring efficient and accurate care delivery in high-stress environments.
4.2. Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma (FAST)
FAST is a bedside ultrasound exam used to quickly identify internal injuries in trauma patients. It focuses on detecting free intraperitoneal fluid, indicating potential hemoperitoneum. The exam evaluates four key areas: the perihepatic, perisplenic, pericardial, and pelvic spaces. This non-invasive method is rapid, repeatable, and highly beneficial in unstable patients. FAST is particularly valuable in emergency settings, guiding immediate interventions like laparotomy. Its integration into EMT training enhances diagnostic capabilities, ensuring timely and accurate trauma care. This tool is instrumental in improving patient outcomes in critical scenarios.
Tools and Technologies in Trauma Care
Modern tools like point-of-care ultrasonography and advanced life support equipment enable EMTs to quickly diagnose and manage trauma patients, improving outcomes in emergency situations with real-time data.
5.1. Point-of-Care Ultrasonography in Trauma Scenarios
Point-of-care ultrasonography (POCUS) revolutionizes trauma care by enabling EMTs to rapidly assess injuries like internal bleeding or organ damage. Handheld devices provide real-time imaging, guiding immediate interventions. This tool is particularly valuable in remote or resource-limited settings, where traditional imaging may not be available. POCUS empowers EMTs to make informed decisions swiftly, improving patient outcomes significantly. Its integration into trauma scenarios enhances diagnostic accuracy and expedites life-saving treatments.
5.2. Advanced Life Support (ALS) Equipment in Simulation Training
Advanced Life Support (ALS) equipment is integral to simulation training, enabling EMTs to practice critical interventions like ventilator management, cardiac pacing, and intraosseous access. High-fidelity simulators mimic real patient responses, allowing EMTs to refine their skills in high-pressure trauma scenarios. Trainees gain hands-on experience with tools like portable defibrillators and infusion pumps, enhancing their proficiency and decision-making; Simulation labs equipped with ALS devices bridge the gap between theory and practice, ensuring EMTs are prepared to operate advanced equipment effectively in emergencies, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Realistic Simulation Exercises
Realistic simulation exercises replicate real-life emergencies, enabling EMTs to practice trauma response in immersive environments. These exercises enhance decision-making, teamwork, and adaptability, ensuring preparedness for diverse scenarios.
6.1. High-Fidelity Mannequins for Trauma Training
High-fidelity mannequins are advanced tools in trauma training, providing realistic patient simulation. These mannequins mimic human physiology, allowing EMTs to practice complex procedures like chest compressions, intubation, and wound management. They offer lifelike responses, such as breathing movements and pulse variations, enhancing the authenticity of training scenarios. Trainees can observe the consequences of their actions in real-time, improving their diagnostic and treatment skills. The use of these mannequins bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, ensuring EMTs are well-prepared for real-life trauma situations.

6.2. Immersive Simulation Exercises for EMT Students

Immersive simulation exercises create realistic, dynamic environments for EMT students to practice trauma care. These exercises replicate real-life scenarios, such as multi-casualty incidents or critical injuries, allowing students to apply skills like patient assessment and stabilisation. Real-time feedback and debriefing sessions help refine decision-making and teamwork. By exposing students to high-pressure situations in a controlled setting, immersive simulations build confidence and competence, reducing errors in real-world emergencies and enhancing patient outcomes.

Emotional Resilience and Stress Management
Realistic simulations prepare EMTs for high-pressure trauma scenarios, fostering emotional resilience. Exposure to intense situations helps build mental strength, enabling professionals to remain calm and focused during emergencies.
7.1. Preparing EMTs for High-Pressure Trauma Scenarios
Preparing EMTs for high-pressure trauma scenarios involves realistic simulations that mimic real-life emergencies. These exercises expose responders to intense situations, helping them develop the mental and emotional resilience needed to stay calm and focused. By practicing decision-making under stress, EMTs build confidence and improve their ability to prioritize patient care. Such training ensures they can effectively manage both the physical and psychological demands of trauma scenarios, ultimately enhancing their performance in critical moments.
7.2. Building Emotional Resilience Through Realistic Simulations
Realistic simulations play a crucial role in building emotional resilience for EMTs. By exposing them to high-stress, real-life trauma scenarios, these exercises help responders develop coping mechanisms and mental fortitude. Simulations mimic the chaos of emergencies, allowing EMTs to practice decision-making under duress. This training fosters emotional stability, enabling them to remain composed during critical moments. Over time, repeated exposure to such scenarios enhances their ability to manage stress, ensuring they can provide effective care while maintaining their own well-being. Emotional resilience is key to thriving in the demanding field of emergency medical services.
